Concrete and paving glossary - F
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M
N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | XYZ

F numbers
The specification of the degree of flatness that a slab or floor must
have. The degree of flatness of a concrete floor is extremely critical
for warehouse or manufacturing plant floors where specialized materials
handling equipment may be guided by wires under the concrete floor.
Face forms
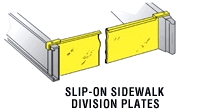
Concrete forms that are used to create a desired curb profile. They
attach to the curb and gutter form set up by hooking to the clips of
the division plate. Face forms are designed based on the amount of batter
specified. See batter, curb
and gutter combination, and curb
and gutter forms.
Faced concrete
To finish the front and all vertical sides of a concrete porch, step(s),
or patio. Normally the "face" is broom finished. See broom
finish.
Fair face concrete
A concrete surface that, on completion of the forming process, requires
no additional (concrete) treatment other than curing. See architectural
concrete and curing.
False set
The rapid development of rigidity in a mixed Portland cement paste,
mortar, or concrete without the evolution of much heat. This rigidity
can be dispelled and plasticity regained by further mixing without the
addition of water. Premature stiffening, and rubber set are terms referring
to the same phenomenon, but false set is the preferred term. See flash
set, Portland cement,
and set.
Fat
Material accumulating on a trowel during smoothing. Fat is used to
fill in small imperfections. See trowel
and troweling.
Fat mix / rich mix
A mortar or concrete mix with a relatively high cement content. Fat
mix is more easily spread and worked than a mix with the minimum amount
of cement required for strength. See cement
and cement mixture.
Fiber reinforced concrete
A variant of concrete that is produced by adding fibers made of stainless
steel, glass or carbon to the mixture. See reinforced
concrete.
Fibrous admixture
Special fibrous substances of glass, steel, or polypropylene that are
mixed into concrete to act as a reinforcement against plastic shrinkage
cracking.
Filler forms
Concrete forming accessories used to connect two metal forms when a
gap between the forms exists. Typically, filler forms have a channel
that slides over the top rail of the forms to be connected. See straight
forms.
Fine aggregate
Aggregate passing the 1/2"
sieve and almost entirely passing
the No. 4 sieve and predominantly retained on the No. 200 sieve.
Fineness modulus
An index of fineness or coarseness of an aggregate sample. An empirical
factor determined by adding total percentages of an aggregate sample
retained on each of a specified series of sieves, and dividing the sum
by 100. Note: US Standard sieve sizes are used: No. 100, No.50, No.
30, No. 16, No. 8, and No. 4, and 3/8 inch, 3/4 inch, 1 inch, 2 inch,
3 inch, and 6 inch.
Finishing
Leveling, smoothing, compacting, and otherwise treating surfaces of
fresh or recently placed concrete or mortar to produce the desired appearance
and service. See also float.
Fixed nose form
A metal concrete pouring form with a fixed nose piece to allow it to
interlock with the rear section of another form creating a solid interconnection.
Fixed nose forms must be removed in order or reverse order after a pour
due to their interlocking nature. See sliding
nose forms.
Flash set
The rapid development of rigidity in a mixed Portland cement paste,
mortar or concrete usually with the evolution of considerable heat,
which rigidity cannot be dispelled nor can the plasticity be regained
by further mixing without addition of water also referred to as quick
set or grab set. See false set.
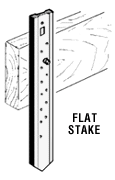
Flat stakes
Flat metal stakes used to secure wooden forms in sandy or loose soils
prior to concrete placement. See curb
and gutter forms, form pins, flatwork
forms, and nail stakes.
Flatwork
Common word for concrete floors, driveways, basements, and sidewalks.
Flatwork forms
Metal or wood forms used in concrete flatwork placement. These forms
are typically used for edge forming, sidewalks, driveways, footings,
industrial slabs, foundations, patios, general flatwork, and in combination
with our curb and gutter accessories, plus concrete curb and gutter
work. See curb and
gutter forms, flexible forms, and
straight forms.
Flexible forms
Metal forms used forming radius shapes such as islands, serpentine
sidewalks, curved curbs, parking lot turnouts, and similar applications.
They are made from spring steel and are typically 10 feet long with
stake pockets riveted onto the form every 18". They range in height
form 4" to 12". The same as radius forms. See spring
steel.
Flexible filler forms
A flatwork form accessory used to fill in spans of less than 10' where
radius forming is required. These forms are sometimes referred to as
rehab forms. See flatwork forms, flexible
forms, and straight
forms.
Float
A tool (not a darby), usually of wood, aluminum, magnesium, rubber,
or sponge, used in concrete or tile finishing operations to impart a
relatively even but still open texture to an unformed fresh concrete
surface. See darby and trowel.
Float coat
A finish coat of cement paste applied with a float. See float.
Floating
The next-to-last stage in concrete work, when you smooth off the job
and bring water to the surface by using a hand float or bull float.
The operation of finishing a fresh concrete or mortar surface by use
of a float, preceding troweling when that is the final finish. See troweling,
float, and float coat.
Floating wall
A non-bearing wall built on a concrete floor. It is constructed so
that the bottom two horizontal plates can compress or pull apart if
the concrete floor moves up or down. A floating wall is normally built
on basements and garage slabs.
Flow-line
The section of a pitch-in curb where water flows in a parallel direction.
See pitch-in.
Fly ash
A byproduct produced by coal-burning power plants that contains aluminosilicate
and small amounts of lime. When combined with lime in a hydrothermal
(using hot water under pressure) process, cement can be produced. It
is a concrete admixture. See admixture.
Footing
The widened portion of the foundation or a structure that spreads and
transmits the load from the building or foundation directly to, and
across a broader area of, the soil. A continuous 8" or 10" thick concrete
pad installed before that supports the foundation wall or monopost.
Form
A temporary erected structure or mold for the support and containment
of concrete during placement and while it is setting and gaining sufficient
strength to be self-supporting.
See corner forms,
formwork, filler forms,
flexible forms, keyway
forms, placement,
radius forms, reversible
forms, straight
forms, slurry, tilt-up
forms, tilt-up
reversible forms, and transition
forms.
Form hanger
A device used to support formwork from a structural framework. The
dead load of forms, weight of concrete, and construction and impact
must be supported. See formwork.
Form pins
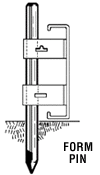 Solid
steel pins made from either cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel used for
securing metal flatwork forms to the ground by driving the pins through
wedge pockets and for attaching screed bar holder clamps used flatwork
finishing. Solid
steel pins made from either cold-rolled and hot-rolled steel used for
securing metal flatwork forms to the ground by driving the pins through
wedge pockets and for attaching screed bar holder clamps used flatwork
finishing.
Pins are typically 1/2" or 7/8" in diameter and vary in length
from 12" to 48" or more depending on the project requirements.
See cold-rolled
solid steel form pins, flat stakes, flatwork
forms, flexible forms, hot-rolled
solid steel form pins, nail
stakes, and screed
bar holder.
Form rail
The top edge of a straight form that runs the length of the form and
is typically 2 inches wide for most standard forms. Often, form rails
are used as guides and supports for screeding. See screeding
and straight forms.
Form release agent or compound
Material used to prevent bonding of concrete to a surface, such as
to forms. See bond breaker,
stripping agent,
and release agent.
Form scabbing
The inadvertent removal of the surface of concrete as a result of adhesion
to the form.
Form stakes
See form pins.
Forming
The use of metal or wood forms to create the proper placement of concrete.
The forming process channels the concrete into the desired shape and
thickness.
See corner forms,
filler forms, flexible
forms, keyway forms,
placement, radius
forms, reversible
forms, straight
forms, slurry, tilt-up
forms, tilt-up
reversible forms, and transition
forms.
Formwork
Temporary structures or forms made of wood, metal, or plastic used
in the placing of concrete to ensure the slurry is shaped to its desired
final form. Formwork must be strong enough to support the considerable
weight and pressure of wet concrete without deflection.
See corner forms,
filler forms, flexible
forms, keyway forms,
placement, radius
forms, reversible
forms, straight
forms, slurry, tilt-up
forms, tilt-up
reversible forms, and transition
forms.
Foundation
The entire masonry substructure below the first floor or frame of a
building, including the footing upon which the building rests.
Foundation form sets
Custom made sets of metal concrete forms used for houses, garage, car
port, strip mall, warehouse floors, and other structures which require
slab on grade foundations. See custom
forms and foundation.
Foundation ties
Metal wires that hold the foundation wall panels and rebar in place
during the concrete pour.
Foundation waterproofing
A high-quality below-grade moisture protection. It is used for below-grade
exterior concrete and masonry wall damp-proofing to seal out moisture
and prevent corrosion. Foundation waterproofing normally looks like
black tar.
Frame
The setting up of formwork. See formwork.
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M
N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | XYZ
|
![]()